The ancient crater Lake Katwe
The ancient crater Lake Katwe
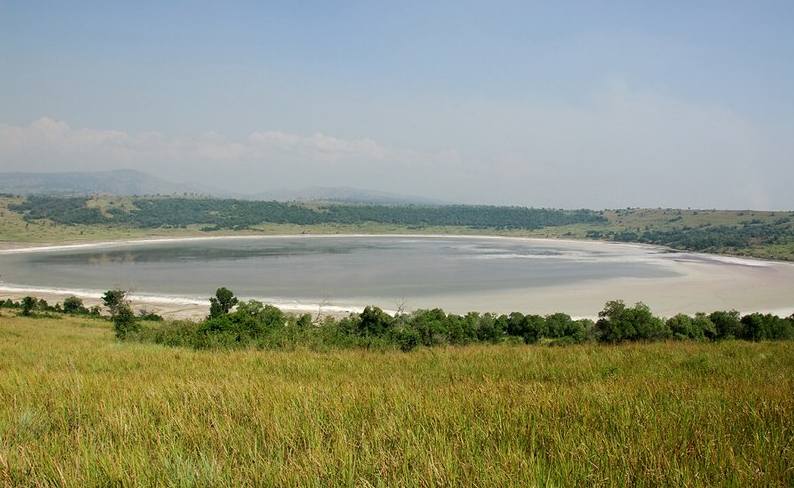
The ancient crater Lake Katwe : this lake was named after the volcanic mountain Katwe-kikorongo, nestled on the Northeastern shores of Lake Edward and south east of Lake George within Queen Elizabeth National park at the bottom of the Western Rift valley on the West side of the Kazinga channel in Kasese district. The lake was formed by a series of violent volcanic explosions that made the crater develop into a salt water lake and despite the process, there was no lava flow. The lake has a variety of water inlets being the main reason as to also why Ocean water is saline or salty. During the dry season; January, February, March, July, August and September there is a lot of evaporation that makes the salt solution concentrated to make salt rocks thus making them the peak seasons for salt mining.

Lake Katwe is served by streams and has no outlet thus making it a very salty lake in this way it is famously known for its quality salt and has been producing high quality salt around East Africa for many years. The lake is a traditional salt mining site where the surrounding communities extract rock salt through a process of constructing semi-permanent pools of water (known as pans) at the mining site to intensify the evaporation therefore making the salt extraction process fast. These pools are around 10 x 12 feet wide as well as 3-5 ft. deep, they are demarcated along the shores of the lake and are privately owned. Salt mining here was started in the 16th century and was discovered by Henry Murton Stanley. A trip to this lake offers an opportunity to learn about the skills of salt mining as well as to interact with the miners regarding their experience in salt mining. The miners use ambatch trees to float on the lake while mining and they also use them to transport the salt to the landing site where it is sold.
There are three main forms of salt mined at the Lake and these are;
Edible salt
- This is the salt that is edible for human beings as its name suggests and is produced through evaporation of water in Katwe’s salt pans.
Crudec (Kihabule)
- This salt is licked by animals and is a by-product of edible salt obtained through a process of preparing edible salt.
Rock salt (mahonde)
- Rock salt is mined by men excavators from the main lake and it is mainly for animal consumption.
Salt mining is rather a risky business to the average human being, in an effort to protect themselves from the toxic water, the excavators have to use all sorts of material to protect their privacy parts lest it leaves them infertile. But despite these worries, they keep mining as they need to earn a living. The women collect off the crusted salt formed on the surface, on the other hand men shovel the salt blocks from the floor of the lake and this is done at the shallow end of the lake. While on your tour to Queen Elizabeth National Park in Uganda, don’t miss to explore this ancient lake.
How to get to Lake Katwe.
Following the route via Masaka road to Mbarara- Masaka road to Mbarara- kasese road taking approx. 7 hours and 17 minutes to reach the lake.










Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!